Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Expert Insights
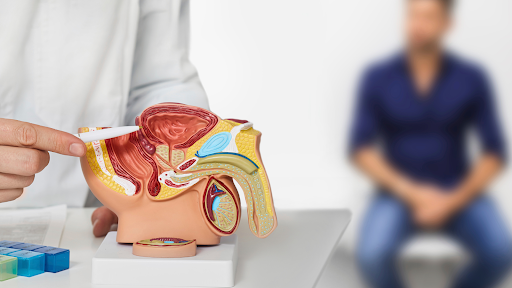
What is Prostate Cancer?
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It produces seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate begin to grow uncontrollably. While many prostate cancers grow slowly, some forms can be aggressive and spread rapidly to other organs.Global and Indian Statistics
- Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide.
- In India, it ranks among the top 10 cancers in men, with rising incidence due to lifestyle changes and improved detection.
Types of Prostate Cancer
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type, originating from glandular cells.
- Small cell carcinoma: A rare but aggressive type.
- Neuroendocrine tumors: Rare and often advanced at diagnosis.
- Sarcoma and transitional cell carcinoma: Extremely rare forms.
Prostate Cancer Symptoms
 In its early stages, prostate cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, common signs include:
In its early stages, prostate cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, common signs include:- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak urine stream or interrupted flow
- Blood in urine or semen
- Painful urination or ejaculation
- Erectile dysfunction
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
Top 10 Signs of Prostate Cancer
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Weak urine flow
- Interrupted stream
- Blood in urine
- Blood in semen
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pelvic discomfort
- Pain in lower back, hips, or thighs
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
Stage 1 Prostate Cancer Symptoms
At stage 1, prostate cancer usually causes no visible symptoms. The tumor is microscopic and confined to the prostate. Most cases are detected during a routine PSA test or digital rectal exam (DRE). Occasionally, very mild urinary changes may occur, but these are more often linked to benign conditions like BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Symptoms
At this stage, cancer is still confined to the prostate but may grow larger. Some men may begin to notice:
- Frequent urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Difficulty starting urination
Stage 3 Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Cancer has spread beyond the prostate to nearby tissues. Symptoms may include:
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Erectile dysfunction
- More severe urinary problems
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Symptoms
This is advanced cancer, often with metastasis to bones or other organs. Symptoms may include:
- Severe bone pain (hips, spine, ribs)
- Swelling in legs due to lymphatic obstruction
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Breathing issues if lungs are affected
Causes and Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer
The exact cause remains unclear, but risk factors include:- Age: Most common in men over 50.
- Genetics: Family history of prostate, breast, or ovarian cancer increases risk.
- Hormonal Influence: High testosterone levels may fuel cancer growth.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, high-fat diet, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
- Ethnicity: Higher prevalence among African-American men.
Stages of Prostate Cancer
Understanding stages helps guide treatment:
- Stage 1: Localized, microscopic, symptom-free.
- Stage 2: Confined to prostate, detectable on tests, may cause urinary issues.
- Stage 3: Spread beyond the prostate to nearby tissues.
- Stage 4: Advanced, metastasized to bones, lymph nodes, or distant organs.
How to Avoid Prostate Cancer (Prevention Tips)
While not completely preventable, risk can be reduced through:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3.
- Limiting red meat, processed foods, and high-fat dairy.
- Regular physical activity and weight management.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol.
- Regular prostate screenings after age 50 (or earlier with family history).
Prostate Cancer Screening & Tests
Early detection is key. Common tests include:
- PSA Test: Measures prostate-specific antigen levels in blood.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): Physical examination of the prostate.
- MRI/Ultrasound: Imaging to detect abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Tissue sampling to confirm cancer.
- Genetic Testing: For inherited risk mutations such as BRCA.
Prostate Cancer Treatment Options
Treatment depends on stage, age, and overall health:
- Active Surveillance: Monitoring slow-growing cancers.
- Surgery (Radical Prostatectomy): Removal of prostate; robotic-assisted options available.
- Radiation Therapy: External beam or brachytherapy.
- Hormone Therapy: Reducing testosterone to slow cancer growth.
- Chemotherapy: For advanced, resistant cancer.
- Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy: New-age treatments improving outcomes.
Signs You Are Dying of Prostate Cancer (Advanced Stage)
This phrase is commonly searched online, but it’s important to approach it with compassion. What it truly refers to are the signs of end-stage or advanced prostate cancer, when the disease has spread widely, treatments may no longer be effective, and palliative care becomes the focus.In this stage, patients may experience:
- Severe bone pain (hips, ribs, spine)
- Extreme fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in legs due to lymphatic blockage
- Loss of appetite and significant weight loss
- Breathing difficulties if cancer spreads to lungs
- Kidney or liver complications due to organ involvement
Complications and Side Effects
- Urinary incontinenceErectile dysfunction
- Infertility
- Bone metastasis
- Emotional stress and depression
Living with Prostate Cancer
- Diet & Lifestyle: Adopt a plant-based diet, maintain healthy weight.
- Exercise: Regular low-impact activities like walking, yoga, and stretching.
- Mental Health: Counseling and support groups can help cope with emotional stress.
- Regular Check-ups: Follow-up appointments and PSA monitoring.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
- Localized cancer: 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%.
- Regional spread: Around 95%.
- Distant metastasis: Drops significantly to around 30%.
Expert Advice from Dr. Gaurav Garg
Dr. Gaurav Garg, with over 15 years of experience in urology and more than a thousand surgeries, emphasizes:
- Regular screening: Essential for men over 50, or earlier if high-risk.
- Lifestyle changes: Diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking/alcohol.
- Early consultation: Immediate medical advice if urinary issues occur.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer is a serious yet treatable disease, especially if diagnosed early. Awareness, screening, and timely treatment are the keys to better outcomes. Don’t ignore urinary symptoms or risk factors.Book your consultation with Dr. Gaurav Garg today on DocGenie to take proactive steps towards prostate health



