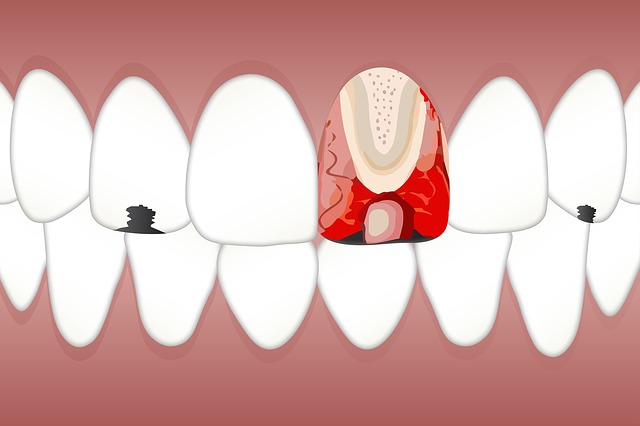
Tooth Cavities Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
3 min read
By DocGenie , Published on - 19 March 2025 Tooth cavities, also known as dental caries, are among the most common oral health issues affecting individuals across all age groups. If left untreated, a cavity can cause discomfort, lead to tooth loss, and even result in more severe health complications. This guide covers the causes, early cavity symptoms, types of tooth cavity, and effective strategies to prevent and manage them—especially for those wondering how to get rid of cavities at home.
Tooth cavities, also known as dental caries, are among the most common oral health issues affecting individuals across all age groups. If left untreated, a cavity can cause discomfort, lead to tooth loss, and even result in more severe health complications. This guide covers the causes, early cavity symptoms, types of tooth cavity, and effective strategies to prevent and manage them—especially for those wondering how to get rid of cavities at home.What Is a Tooth Cavity?
A tooth cavity is a permanently damaged area in the hard surface of your teeth that develops into tiny holes or openings. It occurs when oral bacteria produce acid that erodes tooth enamel. Over time, this damage worsens, especially without proper dental hygiene or professional care.Common Causes of Cavities
 Understanding what causes cavities is key to effective prevention. Here are the primary reasons behind cavity development:
Understanding what causes cavities is key to effective prevention. Here are the primary reasons behind cavity development:- Poor Oral Hygiene: Irregular brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup, leading to decay.
- Sugary and Acidic Foods: Diets high in sugar or acid can erode enamel faster.
- Dry Mouth: Lack of saliva reduces natural cleaning of teeth, increasing cavity risk.
- Bacteria and Plaque: The presence of Streptococcus mutans and other bacteria is a key contributor.
- Frequent Snacking or Sipping: Constant sugar intake gives bacteria more fuel to produce acid.
Early Symptoms of Tooth Cavities to Watch For
 Recognizing early cavity symptoms can help you act before the damage becomes severe:
Recognizing early cavity symptoms can help you act before the damage becomes severe:- Tooth sensitivity when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods
- Visible pits or holes in the teeth
- White, brown, or black stains on the tooth surface
- Mild to sharp pain while chewing
- Persistent bad breath
If you’re experiencing any of these, consider visiting a dentist or exploring sun allergy treatment at home for mild cases—though professional diagnosis is still ideal.
Types of Tooth Cavity
Tooth cavities can form in different areas of the teeth, and knowing the type can determine the right treatment:- Smooth Surface Cavities: These occur on the flat, exterior surface and are the easiest to treat when caught early.
- Pit and Fissure Cavities: Found on the chewing surfaces of the molars; they develop quickly due to trapped food.
- Root Cavities: These affect the tooth roots, common in older adults with receding gums.
Each type needs different attention—while some cavities at home can be slowed with proper care, most require a dentist’s intervention.
What Happens If a Tooth Cavity Is Left Untreated?
Ignoring a cavity might seem harmless at first, but it can lead to several complications:- Infection or abscess formation
- Extreme tooth pain and nerve damage
- Tooth loss and bone deterioration
- Spread of infection to surrounding teeth
Untreated cavities can even affect your overall health, making early detection and management essential.
How to Get Rid of Cavities at Home (Temporarily)
While professional care is necessary for long-term treatment, here’s how to get rid of cavities at home or slow their progress:- Oil Pulling: Swishing coconut or sesame oil may reduce harmful bacteria.
- Fluoride Toothpaste and Mouthwash: Strengthens enamel and reduces decay.
- Avoid Sugar: Cutting down on sugary snacks prevents further enamel erosion.
- Clove Oil: Has analgesic and antibacterial properties; useful for cavity-related pain.
- Healthy Diet: Foods rich in calcium and vitamins support strong enamel.
Keep in mind, these home remedies may only offer temporary relief. For significant damage or persistent symptoms, see a dentist.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Preventing tooth cavities is possible with consistent oral care habits:- Brush Twice Daily Use fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel and prevent plaque buildup.
- Floss Every Day Flossing removes food particles and plaque from between the teeth.
- Rinse With Mouthwash Antibacterial mouthwashes reduce cavity-causing bacteria.
- Regular Dental Checkups Visit the dentist every 6 months for cleanings and early cavity detection.
- Watch Your Diet Limit sugary foods and drinks. Instead, consume more fiber-rich fruits and calcium-rich foods.